
Introduction
Corticosteroids are the first line therapy for autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA), but are associated with significant adverse events, dependency and frequent relapses. Rituximab is reserved for severe or steroid-resistant disease. Low-dose rituximab is also effective, but its efficacy in the first line has been poorly described. We report our results with this combination.
Methods
Adults older than 16 years newly diagnosed with warm antibody AIHA either primary or secondary were included. Patients systematically received dexamethasone 40 mg for 4 days followed by a 1 mg/kg rapid prednisone taper plus rituximab 100 mg weekly for 4 doses. Our primary outcome was response at day 28 based on the First International Consensus Meeting (complete response: normalization of Hb, no evidence of hemolysis and absence of transfusions; response: increase of Hb by >2g/dl, or normalization of biochemical resolution of hemolysis or absence of transfusion in 7 days), secondary outcome was event-free survival with an event defined as a laboratory or clinical relapse or loss of response.
Results
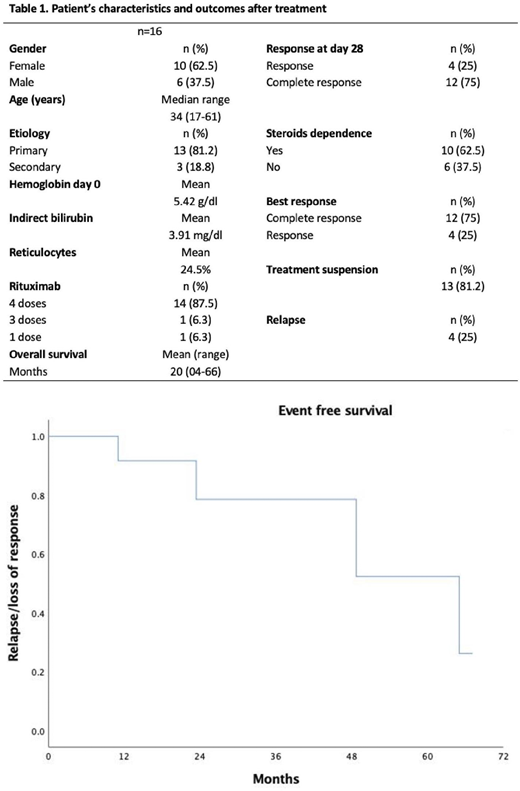
Sixteen patients were treated with low-dose rituximab during the study period, ten women (62.5%), six men (37.5%). The median age was 34 years (range, 17-78). Three (18.75%) were secondary to lupus erythematosus. The median follow-up was 20 months (range, 0.4-66). Most received 4 doses of rituximab (87.5%). All patients responded at day 28, (100%) 31.2% achieved a complete response (CR). Subsequently, 81.3% achieved CR. Ten (62.5%) were considered steroid-dependent, however, most discontinued treatment without loss of response (75%). The event-free survival was 63.8% to 5 years.
Conclusion
Low-dose rituximab therapy as a first-line in AIHA showed encouraging results as most patients were able to discontinue treatment without relapse.
Gomez-Almaguer:Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Celgene/BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; AstraZeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal